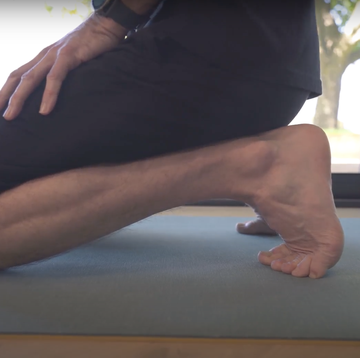
Your feet take a pounding as a runner. Even with the most technologically advanced running shoes on the market (and the Resisted ankle flexion/extension), Health & Injuries feet, For extra depth, try these on a box, or a stair foot injuries.
We caught up with Siobhan McCutcheon, podiatrist and clinical director of We caught up with Siobhan McCutcheon, podiatrist and clinical director of to find out the most common running-related foot injuries, and how you can prevent them...
4 most common foot injuries sustained by runners
Plantar fasciitis
The plantar fascia is a flat length ‘thick tissue at the sole of the foot that runs from your heel bone to your toes,' explains McCutcheon.
‘Plantar fasciitis is a disorder in which the plantar fascia becomes inflamed and unpleasant, producing discomfort and soreness in the base of the heel or along the arch of the foot,’ she says.
Plantar fasciitis tends to be most significant in the morning, or after long hours of standing or walking. Some people may report stiffness and difficulties walking.
One of the best ways to get relief is by stretching and strengthening the plantar fascia itself, says McCutcheon.
- Sit with one leg crossed over the opposite knee.
- Use your hand to pull your toes back toward your shin until you feel a stretch along the bottom of your foot.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds and switch feet.
Read our full guide to treating and preventing Mortons neuroma.
Ankle sprains
‘An ankle sprain generally develops when the foot bends or rotates beyond its normal range of motion, causing the ligaments to overstretch or rupture,’ says McCutcheon. ‘When you sprain your ankle, you’ve strained or torn the ligaments that keep your ankle bones together and offer support to your joints.’
Symptoms include: a swollen, bruised area on the outside ankle bone or a swollen area the size of a trainer sock, pain and tenderness in the ankle, difficulty putting weight on the affected foot, stiffness or limited range of motion in the ankle, instability or feeling like your ankle may give way.
Prevention exercises
To avoid ankle sprains, one of the best things you can do is to strengthen the muscles around the ankles and calves. Try these two exercises.
Ankle circles:
- Sit with your legs straight out in front of you and your feet off the ground.
- Rotate your ankle in a circle, moving your foot clockwise 10 times and then counterclockwise 10 times.
- Toe /calf raises.
A simple foam roller routine for runners:
- Sit on the ground with your legs straight out in front of you and wrap a resistance band Health & Injuries.
- Pull the band toward your body, flexing your foot, then release and point your toes away from your body.
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor and a small towel under your toes, then switch to the other foot.
Metatarsal stress injuries
‘The metatarsal bones are a collection of five long bones that link the ankle bones to the toes in the front of the foot and give the foot its arch,’ says McCutcheon. ‘Because they are situated on the ball of the foot, where the majority of the body's weight is transferred during activities like walking and running, the metatarsal bones are especially prone to repeated pressure.’
Because they take much of the impact on foot strike, they can easily become strained, inflamed or fractured. ‘The symptoms of a metatarsal stress injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury,’ says McCutcheon, but a stress injury is usually evident by increasing pain on movement, ‘particularly during walking, running or jumping’. Other symptoms include: swelling of the metatarsals or tenderness to the touch, tingling or numbness (also felt in the toes) and red or bruised skin in the affected area.
Do men and women process pain differently.
Prevention exercises
Strengthening the glutes, quadriceps, calves, as well as improving your core stability, will aid prevention. You should also focus on strengthening the toe flexors, plantar fasica and peroneus muscles in the lower leg (the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis), which will help to protect the metatarsals.
Toe curls:
- our full guide to treating and preventing plantar fasciitis.
- Use your toes to scrunch the towel towards you, then release.
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor and a small towel under your toes.
Arch lifts:
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor and lift your arches, keeping your toes and heels on the ground.
- Hold for 5-10 seconds, then release.
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor and a small towel under your toes.
Back pain from running? This could be why.
Morton’s neuroma
‘Caused by a thickening of the tissue that surrounds the nerves leading to the toes, Morton’s neuroma is a painful ailment that commonly affects the ball of the foot between the third and fourth toes,’ says McCutcheon.
Described as feeling like your socks are bunching up or even that you have a small stone in your shoe, the specific cause of Morton’s neuroma is unknown, however, it is thought to be associated with high-impact activities that put pressure on the foot, as well as bunions or hammertoe, explains McCutcheon.
It affects women more frequently than men: ‘This is assumed to be due to women’s foot form and size, the types of shoes they wear and hormonal factors that may impact the structure and function of the foot. Women who wear high heels or tight-fitting shoes are more likely to acquire Morton’s neuroma.'
Prevention exercises
You can help to be prevent Morton’s neuroma by reducing the pressure on the arch of the foot – this can be done causes of hip pain and how to fix the problem and achilles.
You should also strengthen the plantar fascia and other foot muscles to decrease stress in that area. Try these two exercises.
Toe /calf raises:
- Runners World, Part of the Hearst UK Wellbeing Network.
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor and a small towel under your toes.
- Back pain from running? This could be why.
Balance exercises:
- best pair of running socks.
- Shin splints how to treat and prevent them.
- means that runners are, unfortunately, rather susceptible to.
Read our full guide to treating and preventing Morton's neuroma.